Python Dictionary
Hello guys, we will be discussing about Python Dictionary. It is an unordered
representation and collection of items. Each item has a key/value pair. They are to obtain value when the key is known.
Initializing
of dictionary
Initializing a dictionary requires the elements to be
in between the {} brackets. Each
item has a key and a corresponding value expressed as a pair. Representation is
shown below,
Output
As seen we have used built-in function, dict(), to create a dictionary.
Accessing elements
from dictionary
We use indexing to access other data types but in
dictionary, we use keys. Keys can be
used either inside square brackets []
or with the get() method.
KeyError
is raised in case a key is not found in the dictionary. On the other hand, the get() method returns None if the key is not found.
Output
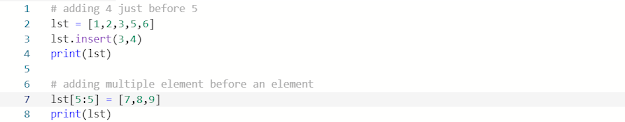
Changing and
Adding of Elements
Dictionaries are mutable. We can
easily add or change items using an assignment operator.
Output
Removal of
Elements from Dictionary
We use pop() to remove a particular item from a dictionary. This removes
an item with the provided key and returns the value. popitem() can also be used,
but this method selects the element randomly and return the item pair from the dictionary.
clear() will empty the dictionary
while del will delete the dictionary or can be used to
delete a specific item.
Output
Python
Dictionary Methods
We have discussed few of the
methods above like pop(), del,
popitem(), get(), clear()
1)
Python
Dictionary fromkeys()
It creates a new dictionary with the sequence of
elements with a value provided by the user.
Syntax is,
|
dictionary.fromkeys(sequence, keys) |
Sequence: - a sequence of elements which is to
be used as keys for the new dictionary.
Value (optional): - values which will be set to each element of
the dictionary by the user.
A dictionary from mutable
object list,
Output
2) Python
Dictionary values()
It returns the list of all the
values in the dictionary.
The syntax is,
|
dictionary.value() |
This doesn’t take any
parameters.
Output
What if the dictionary is
modified?
Output
3) Python
Dictionary update()
The
syntax is,
|
dict.update(other) |
How update() works with an iterable?
Output
4) Python
Dictionary keys()
It returns the list of all the
keys in the dictionary.
The syntax
is,
|
dict.keys() |
This doesn’t take any
parameters
Look for the output on your own for better understanding.
5) Python
Dictionary items()
It returns the list of
dictionary’s tuple pairs.
The syntax
is,
|
dict.items() |
This doesn’t take any
parameters
Look for the output on your own for better understanding.
6) Python
Dictionary setdefault()
The setdefault() method
returns the value of a key. If not, it inserts key with a value to the dictionary.
The syntax
is,
|
dict.setdefault(key, defaultvalue) |
Key: - key to be searched in
the dictionary
Defaultvalue: - key
with a value defaultvalue is inserted to the dictionary if key is not in the
dictionary. If not provided, the defaultvalue will be None.
When
key is the dictionary,
The output will be the value of the key which is 0.
When
the key is not in the dictionary,
Check out the output.
PYTHON DICTIONARY COMPREHENSION
If you still have any doubt on this topic then do come to us via email "sophomoretechs@gmail.com" or via Instagram "@coding.winds".
Do subscribe to our daily blog update by clicking here.
Thank You!